
Moreover a further 28 patients, including three with residual changes at six weeks of follow-up, had further radiology between eight and twelve weeks post admission. In these patients repeat CXR was normal in 56 of 59 (94.9%) two of the three with persistent changes demonstrated atelectasis as well as consolidation. However follow-up CXR was performed at least six weeks after initial imaging in 59 patients, including 5 with changes noted at four weeks follow-up. In those who had a follow-up CXR within four weeks of initial imaging, repeat CXR was normal in 9 of 14 (64.3%). Mean (SD) duration between initial and follow-up CXR was significantly longer in those with normal follow-up CXR findings (mean 10.26, SD 8.03 week), compared to those with persistent residual changes (mean 4.62, SD 5.91 weeks (p value 0.040). Of 161 patients, 93 (57.8 %) had a follow-up CXR, of whom 24 (25.8%) had both consolidation and atelectasis. Of these, 38 (23.6%) had atelectasis and 24 (14.9%) had pleural effusion. We studied 161 patients admitted to paediatric ward with radiological evidence of consolidation between 1st January 2016 and 30th October 2016. We therefore set out to examine the outcomes and timing of follow-up CXR in a group of paediatric patients and whether there is a link between blood tests (serum WCC, neutrophil, platelet, CRP) and radiological evidence of pneumonia. Evidence for benefit of follow-up chest radiograph (CXR) is inconclusive 2-4. Pneumonia is a common paediatric condition with estimated incidence 14.7 in 10,000 in children aged 0–16 years 1. If you have any comments, do send the feedback below.Follow Up Chest Radiography In Paediatric Pneumonia: Is It Avoidable? Next Article will include Chest Xray reading for Pulmonary TB, Collapse, Effusion and Abscess in next article. Most commonly are solitary. Air-bronchograms are often present. Round pneumonias are round-ish and while they are well-circumscribed parenchymal opacities, they tend to have irregular margins. Round Pneumonia ( Rarely important) : Cause Bacterial infection in Children. Reading “Multiple Cystic translucent areas in the RLZ” Features are- smooth inner margins,contain little if any fluid, wall (if visible) is thin and regular, persist despite absence of symptoms. Pneumatocoeles: are intrapulmonary air-filled cystic spaces that can have a variety of sizes and appearances. Reading ” Patchy opacities with peri-bronchial cuffing in the perihilar areas bilaterally”Ĥ. Xray of patient with Mycoplasma with peribronchial cuffing leading to patchy infiltrates”

Bronchopneumonia: usually shows bilateral involvement with patchy infiltrates. Involvement of the supporting tissue of the lung parenchyma resulting in fine or coarse reticular opacities or small nodules.įindings ” Central trachea and Mediastinum, Diffuse fine reticular opacities involving the entire lung field with Normal CP angles and Normal cardiac Shadow”ģ.
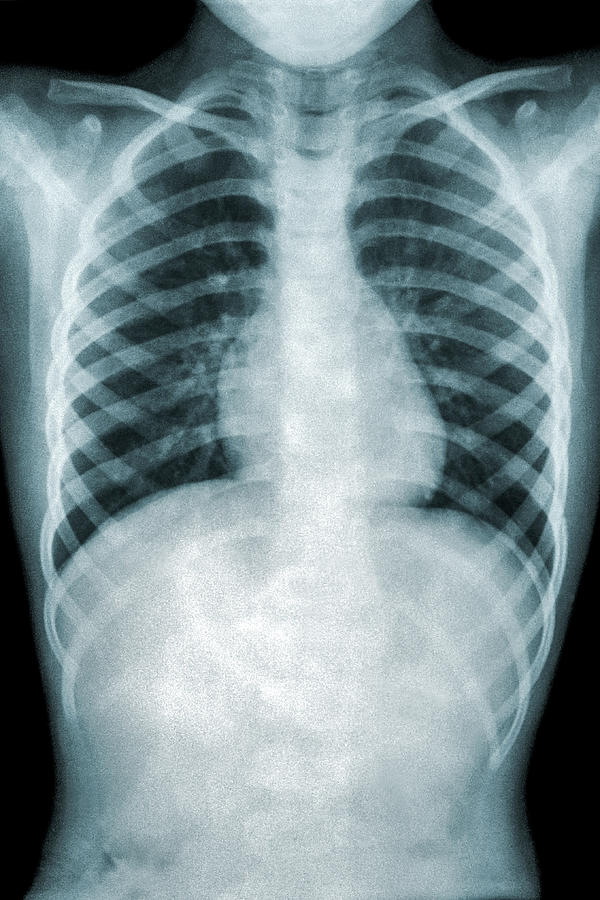
Interstitial pneumonia : Usually Viral, Atypical organisms There is silhouetting of Right cardiac border ( RML pneumonia). There is non-homogenous opacity involving right middle zone with visible air bronchograms and indistinct borders. To the Sequence add the finding ” The Trachea is Central, There is no shifting of Mediastinum, The Costophrenic angles are sharp and clear. Pneumonia Lobar consolidation – usually Streptococcal pathology
#Chest xray pneumonia how to
Before Proceeding to How to Read Chest Xray of Pneumonia patient, read the sequential reading of chest Xray.Īir Bronchogram- air-filled bronchi (dark) being made visible by the opacification of surrounding alveoli (grey/white)ġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
